Agriculture – How Can Farming Be More Sustainable?
Photo Source: Organic Authority
Sustainable agriculture is defined as farming in sustainable ways, which meets the society’s present food needs without compromising the ability for current or future generations to meet their needs (Food Print, 2019). Sustainability has three major components – societal, environmental and economic. Sustainable agriculture must address all three of these parts to be considered sustainable. According to Food Print, the main goals of sustainable agriculture are to provide adequate food for everyone, provide an enhanced standard of living by not being harmful to the environment or depleting natural resources, incorporating farming methods that enhance as well as promote soil health, and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels for a sustainable environment.
There are many ways we can introduce sustainable farming methods. One of the biggest ways to do so is by reducing our reliance on fertilizers and pesticides, and instead focusing on natural processes which can reduce the pest population.
There are several key sustainable farming practices – for example:
Crop rotation
This is the practice of growing different crops on the same piece of land periodically, in a sequence. This helps to improve soil fertility and combat pest and weed control. Good crop rotation is a systematic succession of the three general classes of farm crops, namely, cultivated crops, grain crops, and grass crops.This is practiced in such a way to give large yield and provide pasture and forage on the farm at the least expense of labor and soil fertility (Joe Gardner, 2019).
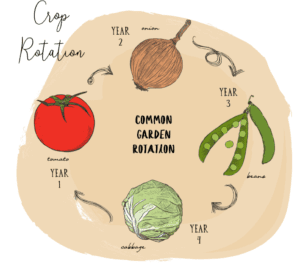 Source: E-Agrovison
Source: E-Agrovison
Natural animal raising
Sustainable livestock farmers use various practices, not only to raise their animals, produce better products and provide a living for their family, but also to build soil and sequester carbon, mitigating the effects of greenhouse gases. With this mutually evolving relationship between animals and grasslands, livestock grazing and pastoral systems enhance the land in multiple ways such as allowing the grasslands to rest and grow, this process accelerates the storage of atmospheric carbon into the plants and soil (World Bank, 2021).

Biodynamic farming
This method of sustainable agriculture incorporates ecological and comprehensive practices that are evolved from the philosophy of “anthroposophy”. According to Pasture to Plate, this method emphasizes the importance of soil health in organic agriculture. Animals are raised in a way that they help in restoring soil fertility and enhance plant growth. Organic manures, rotating complementary crops, composts and sprays are used exclusively, reducing the use of off-site inputs, such as chemical fertilizers and pesticides.

As Ryan from Blue and Green Tomorrow says, sustainable agriculture has a great potential for benefiting the environment and preserving our natural resources. It does so by following natural cycles, recycling nutrients and water, whilst omitting the use of excessive agriculture chemicals.
Sustainable agriculture strives to help our environment by:
- Saving water
- Preventing pollution in rivers and lakes
- Maintaining soil fertility by recycling the nutrients on the farm
- Decreasing emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants
- Ensuring welfare of farm animals and also providing a space for coexistence with the native wildlife
Our wellbeing is closely linked to the health of the environment we live in. The farmers facing poverty are often forced to mine natural resources like soil fertility to make ends meet, even though environmental degradation may hurt their livelihood in the long run. Therefore, we can promote sustainable agriculture systems by creating policies that integrate social, environmental and economic interests.
By Varinddha Thakur
